Understand everything about the thyroid and thyroid hormones: their influence on the human body and their impact on the athlete's life.
The use of this treatment then evolved over time. There was an epidemic of goiter in the Alps where it was first described as a neck tumor in the 14th century.
It was in 1656 that Thomas wharton named the thyroid gland, due to its shield shape. In 1811, in Paris, iodine was discovered in burnt seaweed and it was directly speculated that it was the active ingredient that made the treatment of hyperthyroidism effective.
After 10 years, Proust recommended iodine as a treatment and Robert Graves, meanwhile, published a book on goiter in 1835.
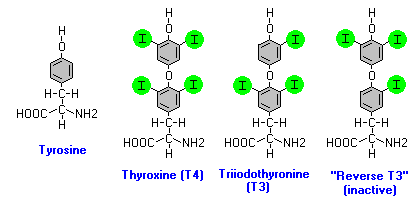
It was in the 19th century that thyroxine (T4) was isolated by Edward Calvin Kendall. CR Harington then synthesized the hormone, followed by T3 which was also isolated and synthesized in turn.
These two hormones have since been constantly improved and made available for the health of all. Today, natural thyroid hormones which contain a mixture of T4 and T3 provide effective treatments for various thyroid hormone disorders.
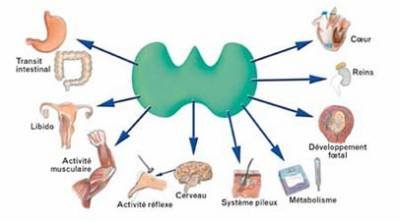
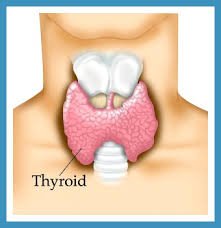
Thyroid hormone is secreted by the butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck, the thyroid, which sits in front of the trachea, and just below the vocal cords or larynx. Although small, the thyroid plays a big role in controlling many of our bodily processes with the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 that it releases, primarily for the regulation of metabolism. You may feel tired most of the time or restless, and lose or gain weight, even with a proper diet.
Your heart rate and body temperature can be raised and lowered. It controls the speed at which food moves throughout your digestive tract, the breakdown of food and convert it into energy, the rate at which your body burns calories, and how quickly cells regenerate and are replenished. .
Thyroid diseases such as goiter, hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, depend on how much or not enough of this hormone is produced.
Production of thyroid hormones
The production of thyroid hormones affects all organs and cells in the body. There are two types of hormones released by the thyroid gland: thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodo-thyronine (T3). The thyroid gland uses two raw materials in the production of thyroid hormones:
Iodine.
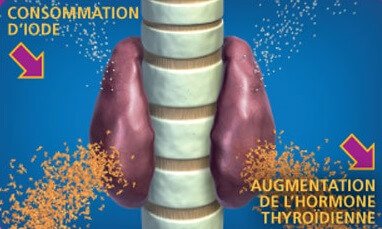
Thyroid cells have a unique specialized function to absorb and use theiodine in its processes. Iodine comes from the food you eat, taken up into the bloodstream by thyroid epithelial cells, which contain a sodium iodide symbol on its outer plasma membrane. Once the iodide is trapped, it is then transported into the lumen of the follicle along with the thyroglobulin.
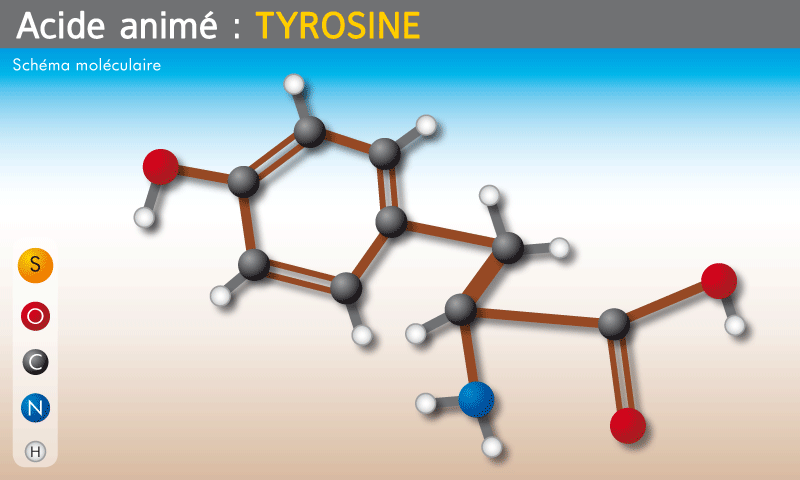
Tyrosines.
These come from thyroglobulin, a large structure of glycoprotein synthesized by epithelial cells of the thyroid gland then secreted into the lumen of the follicle. The tyrosine residues form two groups mono-iodo-tyrosine (MIT) and di-iodo-tyrosine (DIT). Two di-iodinated tyrosines when joined together form thyroxine, and one MIT particle and one DIT particle combined produce tri-iodo-thyronine.
Having an adequate supply of iodine is essential in order to achieve normal levels of thyroid hormone production. Iodine deficiency is said to prevent the thyroid from making thyroid hormones, and could have adverse effects on your body's growth, metabolism, heart rate, other critical functions, and your overall well-being. Iodide is the first to take place in the synthesis, which is then converted to iodine and eventually condensed into tyrosine residues.
The thyroid peroxidase enzyme serves as a catalyst for the iodination of tyrosines on thyroglobulin, and the synthesis of biological agents activates T3 and T4. The reaction with the thyroperoxidase enzyme allows thyroid hormones to accumulate in the colloid of the follicle and then on the surface of the thyroid epithelial cells. These cells ingest the colloid by endocytosis and the vesicles fuse with the endocytosis lysosomes, thus releasing thyroid hormones.
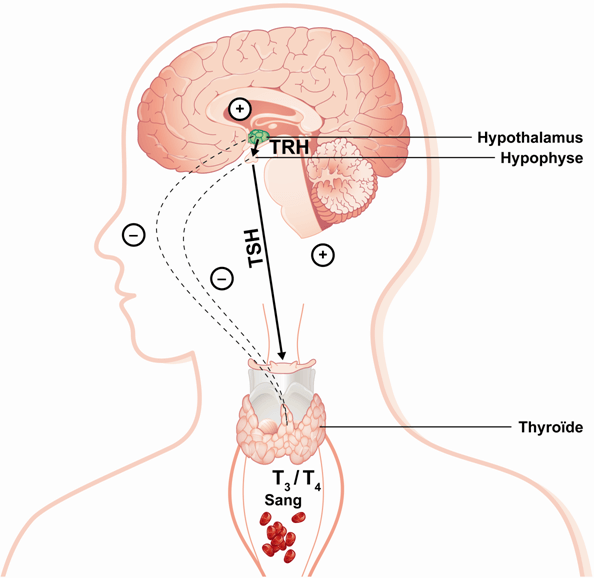
The thyroid gland cooperates with the pituitary gland which releases TSH or thyroid stimulating hormone. The secretion of TSH causes the thyroid gland to release more of it, a high TSH level means there is not enough thyroid and a low TSH means there is too much. The normally functioning thyroid produces around 80% T4 and around 20% T3.
T3: Triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine or T3 is one of two hormones produced by the thyroid gland, the other being T4. T3 is identical to T4, with the particularity of having fewer iodine atoms within each molecule. T3 is the most active hormone produced from T4, which is de-iodized by 3 de-iodinase enzymes.
Triiodothyronine is composed of:
- Type I which is found in the kidneys, liver, thyroid, and pituitary gland.
- Type II found in the CNS, pituitary, vessels of the heart, and brown fatty tissue.
- Type III found in the placenta, the central nervous system, and a hemangioma.
The effects of T3 on target tissues are more powerful than the effects of T4. Most of the T3s in your blood bind to protein, and those that don't do so are called free T3s. Measuring T3 in your blood can help doctors determine if you have a thyroid problem.
Potential disorders are hyperthyroidism when the thyroid produces excessive hormones, hypothyroidism when the thyroid glands do not produce normal amounts of thyroid hormones, periodic thyroid-toxic paralysis which results in muscle weakness or lumpy goiter toxic when the thyroid gland is malfunctioning and having rounded growths.
T4: Thyroxine
It may be weaker than T3, but it produces in significantly higher amounts and has a longer half-life. It is considered the pro-hormone since it acts as a reservoir for T3, where T4 is converted into the tissue your body requires.
Measuring T4 can help diagnose thyroid problems, where symptoms including puffiness, dryness, irritation, swelling, dry skin, hair loss, increased heart rate, weight changes, anxiety, sleep disturbances, fatigue, constipation and irregular periods.
The highs and lows indicated by a T4 test would indicate disorders similar to what doctors can find when running a T3 test.
Medical uses for thyroid hormones
Thyroid hormones are very useful in terms of medical applications. The hormones T3 and T4 are commonly used to treat hypothyroidism, which is a condition caused by the thyroid gland's lack of natural production. Hypothyroidism is normally caused by Hashimoto's disease, inadvertent weakening of the thyroid gland by radiation therapy or surgery, or by drugs that lower thyroid hormone levels.
Hormone therapy of the thyroid is done in the hope of reproducing normal thyroid function. T4, which is pure, and synthetic thyroxine, are the best things to act as a natural thyroid hormone and it works wonders to replace the missing hormone.
Thyroid hormones can be ingested orally and the intestine absorbs them well. They should not be taken more than once a day because the hormones stay inside our body for a long period of time, moreover they appear at very stable levels as they circulate in the blood.
The ultimate goal of thyroid treatment is to maintain thyroid function at the same rate as for people without thyroid problems. The best time to take the TSH is found on getting up in the morning, when you wake up on an empty stomach, since TSH may be more difficult to absorb from food. The key to a well-functioning thyroid is to be consistent in taking the thyroid hormone medication at the same time every day, but be sure to check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medications.
Studies show that patients with hypothyroidism who take thyroid hormones for medical uses get positive changes, which include the following:
- A markedly improved energy level throughout the day.
- Regulation of mood, general well-being and stimulation of mental functions such as memory retention and critical thinking.
- A lower level of triglycerides and cholesterol.
- Normalization of growth in children that has been delayed due to the condition. An immediate growth spurt, as if the thyroid is working again when they take adequate doses.
Sports uses of thyroid hormones
Thyroid hormones are no strangers to the world of sports. Sports and their vigorous and punitive daily training can exhaust the body, and directly affect the thyroid gland. Thyroid hormones come in many forms in this discipline.
Prescription drugs such as pills and tablets to be taken in powder form.It should also be noted that the level of thyroid hormones determines the speed or slowing down of basal metabolism, this is vital information for all runners and bodybuilders.
Putting the body in a situation similar to hyperthyroidism will allow the user to burn more calories in the form of heat, a rise in body temperature called thermogenesis.
There is still an ongoing scientific debate over how thyroid hormones are used as a performance enhancement supplement, as there is also a correlation that intense training can overtax the thyroid gland over time. time. This can easily go against the grain, given the importance and value that the thyroid gland plays in our day to day life.
It is a proven fact that running in endurance mode can reduce the production of thyroid hormone and ultimately the runner or bodybuilder will need to approach a doctor or specialist coach.
Thyroid hormones for weight loss

Thyroid hormone regulates metabolism in humans and animals. Metabolism can be measured by the amount of oxygen that is used by our body in a specific period of time. The BMR or basal metabolic rate, is the figure obtained when the measurement is taken at rest. BMR was one of the primary test indicators to determine whether a patient had an underperforming or over performing thyroid.
T3 is also involved in an important role in increasing a person's BMR. When thyroid hormones are introduced into the system, they increase the rate of metabolism and can:
- Increase the number of calories needed for normal body processes, even when the body and muscles are passive and at rest.
- Increase the distribution and utilization of most of the nutrient macromolecules created in the body.
- Increase the amount of energy and oxygen that our body uses.
- Increase the primary energy generation complex in the body, which is the population of ATPase, sodium and potassium.

Put simply, the T3 in thyroid hormones increases the overall basal metabolic rate which digests all food groups more efficiently, unlocks massive energy for the body to use, and can have a profound and immediate effect in overweight people with hypothyroidism diagnosed or not.
Creating an exercise regimen supplemented with regular supplements of thyroid hormones gives a more effective result because the hormone gives the body an abundance of energy which encourages vigorous movement. Unlike artificial stimulants like synephrine or caffeine, thyroid hormone supplements increase the rate of metabolism without the jitters and do not provide a “crash” when the effects wear off.
It should be noted that the supplement should be taken in moderation and the user should keep in mind not to take too much and enter a state of hyperthyroidism.