Understand how liver contributes in health. Learn all about how to preserve your liver and what products are necessary for a healthy liver.
Introduction
In the upper right quadrant of the abdominal cavity there is a large red mass that does not beat, does not move much, and looks like jelly: this is the liver.
This organ is so important that we would not survive for more than a day or two if it suddenly stopped. Fortunately, it has the ability to rebuild and regenerate itself. Up to two-thirds of the liver can be removed and what is left will return to a normal size within months, thanks to its incredible ability to create new liver tissue from the healthy cells that remain.
The liver helps metabolize fat. It produces bile, which breaks down fat while also working as a filter to cleanse toxins from our blood, and help us feel energized. Optimizing your liver health can help you lose weight and reach your athletic goals.
The essential functions of the liver
- Store vitamins, sugar, and iron to help fuel your body.
- Control the production and elimination of cholesterol.
- Remove waste, drugs and other toxic substances from the blood.
- Produce clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries.
- Produce immune factors and eliminate bacteria from the bloodstream to fight infection.
- Release a substance called “bile” to aid in the digestion of food and to absorb important nutrients.
Metabolic functions of the liver
Hepatocytes are metabolic super workers in the body. They play a critical role in the synthesis of molecules that are used to support homeostasis, during the conversion of molecules from one type to another, and in the regulation of the energy balance.
The main metabolic functions of the liver can be summarized into a few broad categories:
- Carbohydrate metabolism
It is essential to keep blood glucose concentrations at a narrow, normal level. Maintaining normal blood sugar levels for short periods (hours) and long periods (days or weeks) is a particularly important function of the liver. Hepatocytes house many different metabolic pathways and use dozens of enzymes that are alternately turned on or off depending on whether blood glucose levels are rising or falling within the normal range.
. - Fat metabolism
Very few aspects of lipid metabolism are unique to the liver, but most are carried out primarily by the liver.The main examples of the role of the liver in fat metabolism include:
- The liver is extremely active in oxidizing triglycerides for energy. The liver breaks down many fatty acids, more than hepatocytes need, and exports large amounts of acetoacetate to the blood where they can be picked up and easily metabolized by other tissues.
- Much of the lipoprotein is synthesized in the liver.
- The liver is the primary site for converting excess carbohydrates and proteins to fatty acids and triglycerides, which are then exported and stored in fatty tissue.
- The liver synthesizes large amounts of cholesterol and phospholipids. Some are packed with lipoproteins and made available to the rest of the body. The rest is excreted in the bile as cholesterol or bile acids.
- The liver plays a central role in all of the body's metabolic processes.
. - In the fat metabolism, liver cells break down fat and produce energy. They also produce around 800 to 1000 ml of bile per day. This yellow-green, brown, or olive fluid is collected in small ducts and then passed to the main bile duct, which carries the bile to a part of the small intestine called the duodenum. Bile is important for the breakdown and absorption of fat.
. - Carbohydrate metabolism
The liver helps ensure that the level of sugar in the blood (blood sugar) remains constant. If your blood sugar level increases, for example after a meal, the liver removes sugar from the blood and stores it as glycogen. If someone's blood sugar levels are too low, the liver breaks down glycogen and releases sugar into the blood. Along with sugar, the liver also stores vitamins and minerals (iron and copper), and releases them into the blood when needed.
. - Protein metabolism
The liver also plays an important role in protein metabolism: Liver cells change amino acids in food, so they can be used for energy, or to make carbohydrates or fats. A poisonous substance, called ammonia, is a byproduct of this process. The liver cells convert ammonia into a much less toxic substance called urea, which is released into the blood. Urea is then transported to the kidneys and leaves the body in the form of urine.
Hormonal functions of the liver
- The Liver converts thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) in its more active tri-iodothyronine form (T3).
Thyroid hormones act as the body's thermostat, regulating the rate at which almost all biochemical reactions occur in the body. Insufficient conversion of T4 to T3 by the liver can lead to hypothyroidism which depletes energy, leading to chronic fatigue, weight gain, memory loss and a host of other problems.
- Growth hormone (HGH) is produced by the pituitary gland located in our brain.
This hormone causes the secretion of the peptic anabolic hormone IGF-1 (also called somatomedin C), an endocrine hormone produced by the liver, similar to insulin, which only stays in the body for a few minutes, and plays a role influence virtually all muscle systems, bones, connective tissue growth and repair, selectively regulate various aspects of metabolism, as well as help maintain normal brain function and heart health.
Growth hormone (HGH) has a lipolytic (mobilization of fats), hyper-glycemic and diabetogenic action, it stimulates chondrogenesis and osteogenesis via IGF, and it is antinatriuretic. A number of athletes and bodybuilding enthusiasts quickly understood that growth hormone has metabolic effects on their performance gains: increased muscle mass, modification of energy fibers, increased power, anti-aging properties, sexual stimulation.
HGH deficiency in adults results in a metabolic syndrome phenotype, namely increased adiposity, decreased muscle mass, metabolic disturbances, and increased vascular complications.
- Anabolic steroids (AS) are effective in improving athletic performance.
As their use is often associated with increased plasma activity of liver enzymes such as transaminase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (AP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT). These enzymes are present in hepatocytes in relatively high concentrations, and an increase in plasma levels of these enzymes reflects hepatocellular damage or at least increased permeability of the hepatocellular membrane.
In bodybuilding, where usually high doses are used, after stopping the use of steroids, the Gonadotropin (HCG) is often given to stimulate testicular function. The effectiveness of this therapy is unknown.
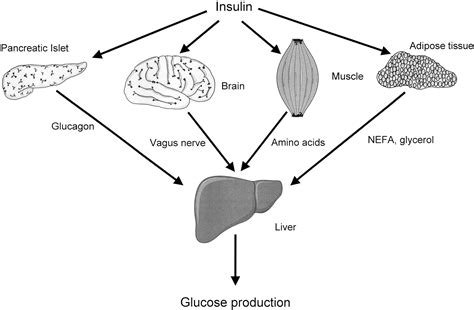
- Insulin is produced by ß cells in the pancreas in response to high concentrations of glucose in the blood.
When a person has not consumed the necessary carbohydrates (sugars) the pancreas will release a hormone called Glucagon to mobilize reserves in the liver. When we work out in the gym, the muscles need nutrients and become sensitive to any amount of insulin. The two main organs that remove excess insulin are the liver and the kidneys. In a non-diabetic patient, the liver removes about 60% of endogenous insulin through the hepatic portal vein while the kidney removes about 35 to 40%.
- The hepatoprotective action of 52 is unmatched in liver care.
The natural ingredients in Liv.52 exhibit potent hepato-protective properties against chemically-induced hepato toxicity. It restores the normal functioning of the liver by protecting the hepatic parenchyma, thus promoting hepatocellular regeneration. The anti-peroxidative activity of Liv.52 prevents the loss of the functional integrity of the cell membrane, maintains cytochrome P-450 (a large and diverse group of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of organic substances), accelerates the delay recovery and ensures rapid recovery of liver function in infectious hepatitis.
- The desmodium is a genus of plants that belong to the Fabaceae family.
Its name comes from the Greek word “desmos”; it means a bond or a chain and it refers to the fruits of the plant. Due to the high content of flavonoids, some species of Desmodium are good for the liver. It improves the condition of our liver and it prevents and fights liver problems like hepatitis or cirrhosis.
The liver is the main organ for the breakdown of hormones after purging their messenger function to their target cells.
For example, if the liver does not process insulin quickly enough, it results in hypoglycemia as insulin continues to lower blood sugar. If adrenaline is not eliminated after fulfilling its role, it can lead to chronic periods of irritability and anger.
Proteins and the liver
The liver is the main regulator of protein metabolism. It converts different amino acids into each other as needed. The liver also synthesizes creatine from the amino acids glycerin, arginine, and methionine. Without the super high energy biochemical creatine phosphate, sprint-like athletics would be biologically impossible.
The main proteins synthesized by the liver are summarized here:
- Albumin - 25% of protein production in the liver
- Globulins - A1
- Haptoglobulins
- Mucoproteins
- A2 - globulins
- Ceruloplasmin
- Glycoprotein
- Macroglobulin
- Plasminogen
- Prothrombin
- b-globulins
- Low (LDL) and very low density (VLD) lipoproteins
- Transferrin
- Blood clotting factors *
- Factors I, II, V, VII, VIII, IX and X
One of the main functions of the liver is to produce proteins secreted in the blood. Plasma proteins are made up of many known proteins, including albumin, fibrinogens, and apolipoproteins. Factors involved in hemostasis and fibrinolysis including coagulation factors, antitrypsin and plasminogen, are secreted into the blood, as well as transport proteins such as transferrin and retinol binding protein. Examples of plasma proteins include APOB, APOA1, FGG, C2, KNG1 and FGA.
According to the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) and the American Dietetic Association (ADA), protein requirements increase slightly in very active people:
For endurance athletes, protein requirements are 1,2-1,4g per kg of bodyweight per day, while those for resistance sports and muscle building can be as high as 1,6 at 1,7 g per kg of body weight per day.
These recommended protein intakes can generally be provided through diet alone, without the use of protein or amino acid supplements, if energy consumption is sufficient to maintain body weight.
The ACSM and ADA also claim that quality protein eaten after exercise will provide amino acids for building and repairing muscle tissue.
Athletes should consume a mixed meal providing carbohydrates, protein and fat soon after an intense competition or training session.
The importance of the liver for athletes
A healthy liver is essential for optimal performance. Good liver function is necessary for burning fat, increasing muscle mass, and providing energy.
The liver clears toxins and manages the processing of proteins and fats. A healthy liver burns fat and provides protein to build muscle.
A weak liver, or a liver that is overwhelmed with toxins and stress will not be able to perform these tasks effectively.
Eating a healthy diet, being aware of the amount of pills you ingest, and a few liver supplements of choice, can keep you strong, burn fat effectively, and keep your liver in good shape for years to come.
Here are some steps every athlete can take to preserve the liver and keep it functioning properly:
- Avoid alcohol and tobacco
- Get enough sleep, which helps build a stronger immune system
- Monitor protein intake, especially for bodybuilders and weightlifters
- Consume high quality supplements that are useful for liver recovery such as high quality multi vitamins and milk thistle.
- Closely monitor your use of performance-enhancing drugs. Steroid users in particular should visit their doctor annually to examine the liver enzymes.
- Avoid daily consumption of NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and acetaminophen)
- Exercise regularly ... exercise is very important for good liver function
- Adopt a diet that promotes liver health
- Avoid dehydration. It is imperative to stay hydrated. And don't underestimate the benefits of good, old-fashioned pure water.
Liver disease
Although liver disease is typically related to alcohol or drugs, the truth is that there are over 100 known forms of liver disease caused by a variety of factors that affect us all from babies to people. elderly.
Here are a few :
- Hepatitis
- Biliary atresia
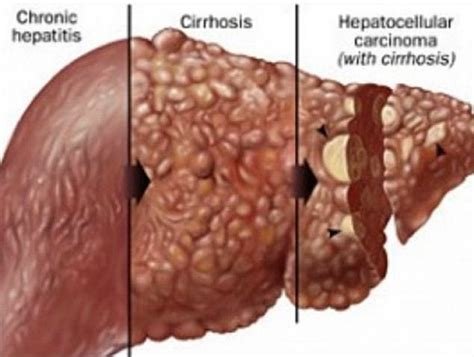
- Cirrhosis
- Cystic liver disease
- Steatosis of the liver
- Galactosemia
- Gallstones
- Gilbert syndrome
- Hemochromatosis
- Liver cancer
- Liver disease during pregnancy
- Neonatal hepatitis
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- porphyria
- Sarcoidosis
- Toxic hepatitis
- Glycogenosis Type 1
- Viral hepatitis A, B, C
- Wilson's disease
- Viral hepatitis
The liver and alcohol
Factors such as gender, age, nationality, weight, and health can affect the way a person's liver metabolizes alcohol. When the liver has too much alcohol to handle, normal liver function can be interrupted leading to chemical imbalance.
Alcohol turns some liver cells into fat and damages others.
Alcohol is easily absorbed through the digestive tract, and up to 98% is metabolized in the liver. Each liver cell contains three pathways for alcohol metabolism.
With regular use of alcohol, this regenerative ability can be inhibited and lead to liver damage. Long-term heavy alcohol consumption can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver, which can progress to alcoholic hepatitis, or lead to cirrhosis of the liver.
This is why it is important to respect the guidelines for sensitive consumption and to spend at least two days a week without alcohol.
The maximum recommended for men is 4 standard drinks per day. For women, 2 standard drinks per day.
A standard glass contains 10 grams of alcohol, and is equivalent to a regular beer or a small glass of wine (100 ml).
More than 6 standard drinks per day for men, and 4 standard drinks for women, becomes dangerous for the liver. The long-term effects of alcohol on the liver are severe pain, inflammation (hepatitis) and cirrhosis.
Why and how to protect your liver
The liver is a wonderfully complex organ that nourishes and protects your body day in and day out. It helps neutralize and eliminate toxins, gives your body the energy it needs to function, fights viruses and infections, regulates sex hormones, cholesterol, vitamin and mineral levels in your body.
In order to maintain the health of your liver, it is important that you understand the crucial roles the liver plays in maintaining your overall health and what activities you can take for granted that can help or harm this vital organ. . By educating yourself more about your liver and how to keep it healthy, you can actually help reduce your risk of developing not only liver disease, but other health conditions, including diabetes and heart disease. .
Health, Lifestyle
Healthy eating and regular exercise help the liver to work well. An unhealthy diet can lead to liver disease. For example, a person who eats a lot of fatty foods is more at risk of being overweight and having non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Your food
Eat foods from all groups: grains, proteins, dairy products, fruits, vegetables, and fats.
Eat foods that are high in fiber, such as whole grain breads, rice, and grains.
Consume fat in moderation and choose “good” ones, such as olive and canola oils, nuts and seeds.
Limit the amount of alcohol you drink.
Alcohol can damage or destroy liver cells. Liver damage can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver (fatty liver), inflammation or swelling of your liver (alcoholic hepatitis), and / or scarring of your liver (cirrhosis). For people with liver disease, even a small amount of alcohol can make it worse. Talk to your doctor to assess how much alcohol is right for you.
Protective agents for the liver
- The Samagen, a vegetarian agent of milk thistle extract (Silybum marianum) in the composition of Samarin, protects the liver from all harmful influences and promote the recovery of healthy cells in the liver.
- Legalon® (MZ 80) helps maintain good liver function. Legalon contains the patented extract of Silybum Marianum (milk thistle) which was developed by the German herbal medicine manufacturer Madaus, in 1968. Clinical trials have shown that Legalon supports liver health by:
- Inhibition of inflammatory cell activation
- Inhibition of oxidative stress
- Inhibition of activation of hepatic stellate cells that cause fibrosis
- Helps in the renewal of normal and healthy liver cells.
- Manage your medications. When drugs are taken wrongly - by taking too much or even mixing them up, the liver can be damaged. Learn about medications and how they can affect the liver. Follow the dosage instructions. Talk to a doctor or pharmacist often about any medications you are taking.
- Avoid breathing or touching toxins. Toxins can injure liver cells.
- Limit direct contact with toxins from cleaning products and aerosols, insecticides, chemicals and additives in cigarettes.
- Do not smoke
How to cleanse your liver
Your liver is a bit of a cleanser for the body. It cleans the blood of all the toxins that we absorb and keeps the internal systems functioning properly.
Modern diets, environmental pollutants, and our increasing reliance on toxic household and personal care products have caused our livers to work a lot of overtime and struggle to keep pace. For this reason, it is important to know how to cleanse the liver in a thorough, effective and natural way.
The thousands of enzyme systems that are responsible for virtually all activities in the body are built in the liver; proper functioning of the eyes, heart, brain, joints and kidneys depends on healthy liver activity. If the liver stops building even one of the thousands of enzyme systems the body needs, there is an impairment of the body's overall function and greater metabolic stress on the individual.
You can try a quality liver detox supplement, or you can use certain items found at your local health food store, your grocery store, or even some that are already in your kitchen.
Here's how to cleanse your liver with 5 common foods
- Lemon and hot water - hot water and lemon is a great way to detox your liver every morning. It's not lemonade, so there's no need to add sugar or anything. Just plain water and a good dose of fresh lemon juice.
- Ail - Add a little garlic to your cooking or slice a clove in your next salad. Garlic contains sulfur compounds which can help activate enzymes in the liver. It contains allicin and selenium, both of which are effective in protecting the liver.
- The lawyers - As if you needed another reason to add avocados to your diet, a Japanese study found that avocados contain compounds that can protect the liver. Compared with 21 other fruits, avocados had the most promise for protecting the liver against galactosemia, a “potent” toxin that damages the liver much like human viral hepatitis.
- Coriander - This versatile herb can be added to just about any dish, including salads or smoothies. This herb can help remove heavy metals from the body.
- Turmeric - Another powerful spice with a long list of benefits, turmeric not only protects the liver from damage, but also promotes regeneration of liver cells. In addition, it increases the production of bile and helps flush out toxins.
Cleaning your liver is essential, so don't hesitate to incorporate these cleaning solutions today.
Conclusion
The link between good health and good nutrition is well established. Interest in nutrition and its impact on athletic performance is now a science in itself.
Living a healthy lifestyle is one way of life that lowers the risk of becoming seriously ill. Not all illnesses are inevitable, but coronary heart disease, and lung cancer in particular, can be prevented.
Health is not only to avoid illness but also to preserve physical, mental and social well-being. Whether you are a competitive athlete, a weekend sportsman or an everyday amateur athlete, the basis for improving performance is a balanced diet.




5 Comments
Hello!
I will need advice, only about 5 years ago that I no longer use drugs, alcohol and even cigarettes, but I had a back accident. I have 2 herniated discs, but slowly I started to train again the problem is that I take 100 mg of oxyneo 2 times a day and dilaudil 4 mg 5 times a day. for the pain more d have had a vasectomy can I take D-bol an answer please Would be appreciated
Hello,
In order to better help you, we invite you to contact our professional coach for any advice on our products and cycles: https://upsteroide.to/conseils-cure//
He will be happy to advise you free of charge to achieve your goals
Hello,
What are the symptoms of a liver having problems? Pains? Penalties? Color of urine? I'm asking these questions because I'm new to it, and I can't find enough competent people around me to ask these questions.
I take Winstrol 50mg / day with Legalon, and unfortunately I don't have enough Legalon to last until the end of my cycle. I still have two weeks of treatment left and if I order more, I will only have it in 3 weeks. So I will continue my treatment without Légalon.
Hello,
In order to better help you, we invite you to contact our professional coach for any advice on our products and cycles: https://upsteroide.to/conseils-cure//
He will be happy to advise you free of charge to achieve your goals
We don't have twice! It is an organ necessary for the proper functioning of the body, so it is imperative to think about protecting it.